In this popular article series, we are exploring the capabilities of Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control 13c for the private Database-as-a-Service (DBaaS) cloud – including the setup of such a cloud. In the previous parts, we started the setup of the private DBaaS cloud, including the configuration of the self-service portal. The full procedure includes setting up the Enterprise Manager software library, creating the PaaS infrastructure zones, database pools, and quotas for the users, service templates, and optionally chargeback plans to apply to the users for cloud allocation and cloud usage.
We configured the software library, set up the Enterprise Manager self update system, and downloaded the latest plug-ins from the external Enterprise Manager store. We created a custom cloud role in Enterprise Manager, and a Cloud SSA user named as "SAI_DAS". Next, we created a PaaS Infrastructure Zone named as “Sainath_PaaS_Zone”, a group of hosts that will be used for Database as a Service. Members (hosts) were added to the PaaS Infrastructure Zone.
After the PaaS Zone, a new database pool was created – a group of database servers where the database software had been pre-installed, with all servers in the pool belonging to the same platform as well as the same database version. Next, we added our Oracle Home targets to the pool, with each Oracle Home target belonging only to a single database pool.
After the database pool was created, we entered the quotas for the role selected. The Quotas page allows the SSA Administrator to configure the total amount of resources which are allocated to the self-service user via the role. Quotas are an important aspect of the cloud and are required in order to control the usage of the self-service cloud. In our case, we assigned the Memory quota as 16 GB, the Storage quota as 100 GB, the number of Database Requests as 10, the number of Schema Service Requests as 50, and the number of PDB Service Requests as 25. This is the total amount of resources that can be utilized by any SSA user to whom the custom role is assigned.
Next, we selected Data Sources from the left panel, and on the page that appears, clicked on the Data Profiles tab and created a new profile. In the creation wizard that started, we selected the Reference target as the “saiprod” database. This is the production database that will be used as the master source. We chose to include “Data Content” and “Structure and Data” by creating an RMAN backup from the source database. The profile will be used for the Database-as-a-Service functionality. You can set the schedule to repeat the profile creation at an interval; this means a new backup will be taken repeatedly, and can be selected by the self-service user.
The database profile has been created. However, if in the future there is new or changed data in the Saiprod database, then, as the cloud administrator, you would want any such data to be made available to the self-service user for creating a copy of the Saiprod database. In this case there is no need for you to recreate the entire profile, since there is a “Refresh Profile” capability which will create a new RMAN Full Backup with the changed data. This new backup version can be selected by the SSA user at the time of self-service of the single instance database.
We then started to create a new database profile to be used for the Snap Clone functionality. We clicked on “Create” in the Data Profiles tab and specified the reference target again as the “saiprod” database, and included the “Structure and Data” by including an “RMAN Database Image” for this new profile, instead of an RMAN backup. This profile will be used for the Database-as-a-Service functionality using the Snap Clone functionality. If the production data has changed, the cloud administrator can click on “Refresh Profile” at any time after the profile creation; this will create a new RMAN Datafile Image backup.
The next step was to create service templates for the database cloud, which can then be used by the SSA User to provision databases in the pool. The profiles created in the previous section are like gold copies of an Oracle database, and they are used by service templates. The service template is what is offered to the SSA user and forms the basis of the functionality of the cloud. However, before a service template can be created, we had to set up multiple “Database Sizes”. These will be used to override the initialization parameter values in the service template once associated with that template. We used the create_database_size verb (explained in the EMCLI [Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface] documentation) to specify multiple database sizes.
Next, we started to create the service templates by selecting Setup | Cloud | Database and then Service Templates in the left pane, followed by clicking on the Create button. We named the service template as “Sainath 11204 Single Instance Database”. Under the Source Identification section, we selected the Create Database as “Using Profile” and then from the list of profiles, we selected the appropriate profile that was created with an RMAN Full backup. This is shown in Figure 23 below.
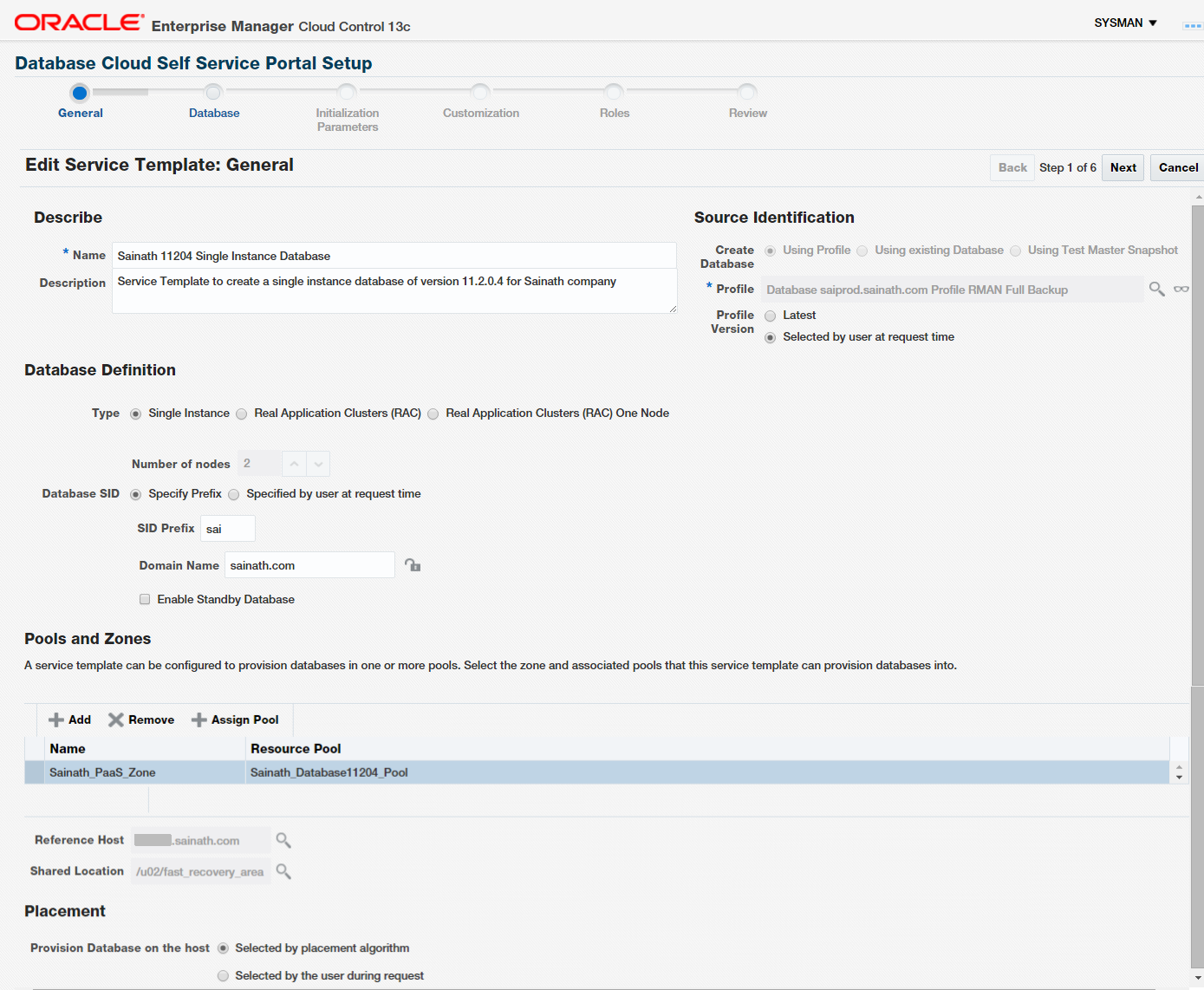
Figure 23: Create a Service Template
This profile with its reference information is now associated with the service template you are creating. If the profile contains data, the data will also be copied when the service template is executed.
As the Profile Version, choose “Selected by user at request time”. This will allow the SSA user to select any of the available RMAN backups that have been created by refreshing the profile. If you select “Latest” on this screen, only the latest backup will be available to the SSA user.
The other options for Create Database, besides “Using Profile”, are “Using existing Database” and “Using Test Master Snapshot”. Test Master Snapshots are a snapshot of an RMAN image backup from a production database. Test Master Snapshots are new in Enterprise Manager 13.1, and can be used to create snap clones. However, these require special storage hardware, such as NetApp Storage Appliance, Sun ZFS Storage Appliance, Dell EMC Storage Array, or even the Solaris File System (ZFS). Note that the dNFS file system and CloneDB cannot be used for Test Master Snapshots.
We will continue in the next part of this article series.
Start the discussion at forums.toadworld.com